HetaSimulator is an open-source simulation and parameters estimation (fitting) platform for the Heta modeling language. The main purpose of the package is to establish the linkage between emerging QSP frameworks and fast computational methods (parallel simulations, automatic differentiation, etc.).
Introduction
Heta language is a domain-specific modeling language (DSL) for dynamic models used in quantitative systems pharmacology (QSP) and systems biology (SB). Heta models can be translated into variety of formats like Simbiology, Matlab, mrgsolve, DBSolve and many others.
This package provides the Julia-based simulation engine for Heta-based models and modeling platforms. Users can simulate QSP models in heta format as well as ODE systems in general form using HetaSimulator without additional tools.
The main features of the package are
- rich capabilities for estimating parameters' values based on experimental datasets
- working with multiple models including multi-scenarios fitting
- parallel simulations
- storing data and scenarios in the unified formats
- datasets and scenarios import from CSV/Excel tables
- full Heta standard support
- storing models, scenarios and data in the
Platformobject for easy management of platform components - utilizing the features of open-source projects like Julia and SciML ecosystem.
Installation
It is assumed that you have Julia installed. The latest Julia release can be downloaded from julialang.org
To install or update HetaSimulator run the code below in Julia environment:
julia> ]
(@v1.10) pkg> add HetaSimulatorInternally HetaSimulator installs Heta compiler as an artifact.
Basic usage
Create a model in Heta format or use your Heta-based platform. Here we will use an example model with two species and one reaction.
// index.heta file in directory "my_project"
comp1 @Compartment .= 1.5;
s1 @Species {compartment: comp1, output: true} .= 12;
s2 @Species {compartment: comp1, output: true} .= 0;
r1 @Reaction {actors: s1 => s2, output: true} := k1 * s1 * comp1;
k1 @Const = 1e-3;To read more about Heta Heta specifications
using HetaSimulator, Plots
# set the absolute or relative path to the project directory
platform = load_platform("./my_project")
# wait for the platform compilation...
# get the default Heta model
model = platform.models[:nameless]
# single simulation and plot
results = Scenario(model, (0., 1200.)) |> sim
plot(results)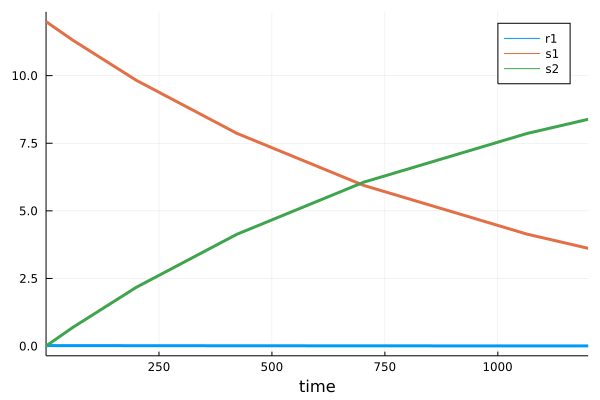
# transform results to data frame
df = DataFrame(results)
...
9×4 DataFrame
Row │ t s1 s2 scope
│ Float64 Float64 Float64 Symbol
─────┼─────────────────────────────────────────────
1 │ 0.0555525 11.9993 0.000666611 ode_
2 │ 0.611077 11.9927 0.00733069 ode_Architecture
The user of HetaSimulator typically deals with the following three types:
Model- an ODE model, containing rhs, rules, initial parameters and vector of events.Scenario- scenario representing a specific model's setup for simulations or fitting. This setup can include initial parameters and events, output variables etc. In case of fittingScenarioshould also include experimental data. A common usage ofScenariocan be model's simulation with different drugs (parameters and events setup). DifferentScenario's can be united to run multi-scenarios simulations and fitting.Platform- container for differentModels andScenarios.
The user can perform the following three operations with both Model, Scenario and Platform
sim- run a single or multi-scenarios simulations.fit- fit a model to experimental data.mc- run Monte-Carlo or virtual patients simulations.
See documentation for detailed overview of HetaSimulator types and functions' arguments.
Getting help
- Read the docs
- Use Gitter Chatroom.
- Use Issue Tracker
License
This package is distributed under the terms of the MIT License.
Copyright 2020-2024, InSysBio LLC
Authors and history
- Ivan Borisov
- Evgeny Metelkin